AngularJS Knowledge Summary
Introduction:
Recently I am working on front end programming, and by chance I started using AngularJS. Frankly it’s a bit mysterious in the first bite. This post show my personal understanding about the AngularJS framework and component relationship.
AngularJS Overview
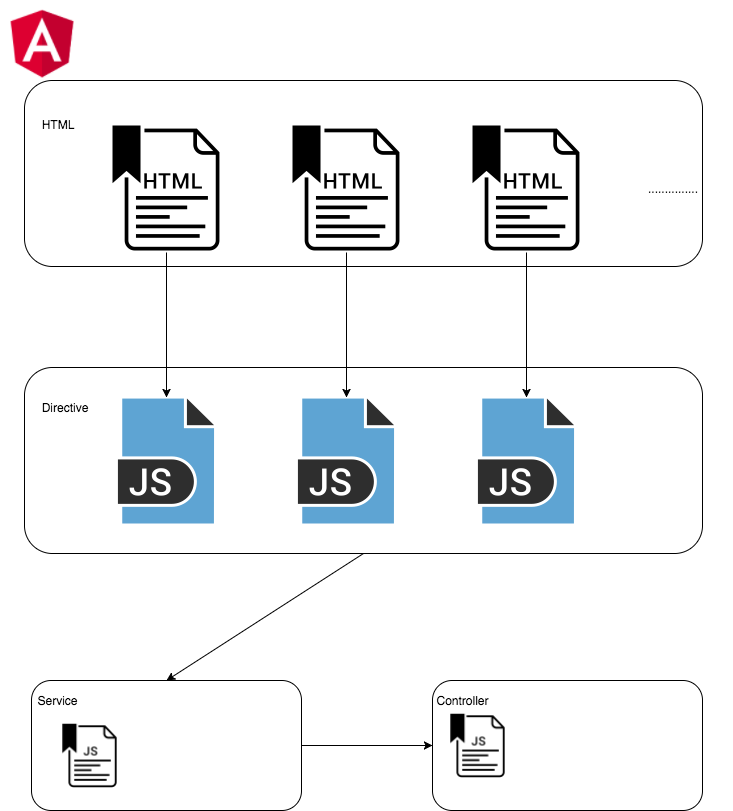
Above is the component relationshio of AngularJS. Each HTML has their own directive.js. And each directive.js are independent. All the directives are able to call the services.js, and service.js is able to call the controller. (Bit complex, just see the graph).
Scope
Angular has many mysterious word. scope, resource, … They are all special in the angular world. Let’s see scope first.
Scope is a way js interact with html. For example,
Resource
Resource is a special call in angular. It means all REST Endpoint resource. Usually we define how to make the Endpount call in the resource.js.
Promise
Because Javascript only has one thread. When we make HTTP call (or any network asynchronous call), angular use a promise to ‘hold the seat’, when the respond comes back, it feeds the seat.
scope.flag = true;
scope.total = 100;
This will set the corresponding value in the front end to specific values.
Pass data through html
If we want to transfer some data from one html page to another, these data are also included in the scope.
<testModal current-data="passData"></testModal>
For example, in the current page (there is an object called currentData), add the above line in the end of corresponding html page, note it must follow the html data passing name format, so it should be current-data. Name passData as the received name.
Then declare which directive will take the data.
angular.module("app.test").directive("testModal")
Then you can easily use ‘passData’ in the corresponding html and js. The passData is saved in scope.
Remember that passData is in scope. So in html page, we are able to use ‘passData’ directly, in the corresponding js, we should use
scope.passData
Special symbol
For data binding, there are different ways of data binding.
> is not in the documentation
< is for one-way binding
@ binding is for passing strings, also, can be used for passing method
= binding is two-way binding
Link, compiler, controller
Compiler compiles the template to be used throughout the page. Linker is tied to each instance. Controller works between instance.